ADO.NET's DataSet
last modified July 6, 2020
The ADO.NET architecture consists of two central parts. The .NET Data
Providers and the DataSet. The data providers are components
that have been explicitly designed for data manipulation and fast access to data.
The DataSet is created for data access independent of any data source.
It can be used with multiple and differing data sources, with XML data, or used to
manage data local to the application.
A DataSet is a copy of the data and the relations among the data from
the database tables. It is created in memory and used when extensive processing
on data is needed or when we bind data tables to a Winforms control. When the
processing is done, the changes are written to the data source. The DataSet
is a disconnected relational structure. This means that the underlying connection
does not have to be open during the entire life of a DataSet object. This enables
us to use efficiently our available database connections.
A DataSet can be populated in a variety of ways. We can use the
Fill method of the SqliteDataAdapter class. We can
create programmatically the DataTable, DataColumn,
and DataRow objects. Data can be read
from an XML document or from a stream.
A SqliteDataAdapter is an intermediary
between the DataSet and the data source. It populates a
DataSet and resolves updates with the data source.
A DataTable is a representation of a database table in
a memory. One or more data tables may be added to a data set. The
changes made to the DataSet are saved to
data source by the SqliteCommandBuilder class.
The DataGridView control provides a customisable table for
displaying data. It allows customisation of cells, rows, columns, and borders
through the use of properties. We can use this control to display data
with or without an underlying data source.
Creating a DataTable
In the first example, we will work with the DataTable class.
sqlite> CREATE TABLE Friends2(Id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, Name TEXT);
In this case, the table must be created before we can save any data into it.
Option Strict On
Imports Mono.Data.Sqlite
Imports System.Data
Module Example
Sub Main()
Dim cs As String = "URI=file:test.db"
Using con As New SqliteConnection(cs)
con.Open()
Dim table As New DataTable("Friends2")
Dim column As New DataColumn
Dim row As DataRow
column = New DataColumn()
column.DataType = System.Type.GetType("System.Int32")
column.ColumnName = "Id"
table.Columns.Add(column)
column = new DataColumn()
column.DataType = Type.GetType("System.String")
column.ColumnName = "Name"
table.Columns.Add(column)
row = table.NewRow()
row("Id") = 1
row("Name") = "Jane"
table.Rows.Add(row)
row = table.NewRow()
row("Id") = 2
row("Name") = "Lucy"
table.Rows.Add(row)
row = table.NewRow()
row("Id") = 3
row("Name") = "Thomas"
table.Rows.Add(row)
Dim sql As String = "SELECT * FROM Friends2"
Using da As New SqliteDataAdapter(sql, con)
Using cb As New SqliteCommandBuilder(da)
da.Fill(table)
da.Update(table)
End Using
End Using
con.Close()
End Using
End Sub
End Module
In the example, we create a new DataTable object. We add two
columns and three rows to the table. Then we save the data in a new
Friends2 database table.
Dim table As New DataTable("Friends2")
A new DataTable object is created.
column = New DataColumn()
column.DataType = System.Type.GetType("System.Int32")
column.ColumnName = "Id"
table.Columns.Add(column)
A new column is added to the table. We provide a data type and
name for the column. The columns of a DataTable
are accessed via the Columns property.
row = table.NewRow()
row("Id") = 1
row("Name") = "Jane"
table.Rows.Add(row)
A row is added to the table. The rows of a DataTable
are accessed via the Rows property.
Dim sql As String = "SELECT * FROM Friends2" Using da As New SqliteDataAdapter(sql, con)
The SqliteDataAdapter is an intermediary between the
database table and its representation in the memory.
Using cb As New SqliteCommandBuilder(da)
The SqliteCommandBuilder wraps the data adapter.
It only needs to be instantiated. We do not work with it directly
later.
da.Fill(table) da.Update(table)
The data adapter is filled with the data from the table. The
Update method inserts the data to the database.
Saving XML data
Data from the DataTable can be easily saved in
an XML file. There is a WriteXml method for this task.
Option Strict On
Imports Mono.Data.Sqlite
Imports System.Data
Module Example
Sub Main()
Dim cs As String = "URI=file:test.db"
Using con As New SqliteConnection(cs)
con.Open()
Dim stm As String = "SELECT * FROM Cars LIMIT 5"
Using da As New SqliteDataAdapter(stm, con)
Dim ds As New DataSet()
da.Fill(ds, "Cars")
Dim dt As DataTable = ds.Tables("Cars")
dt.WriteXml("cars.xml")
For Each row As DataRow In dt.Rows
For Each col As DataColumn In dt.Columns
Console.Write(row(col) & " ")
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Next
End Using
con.Close()
End Using
End Sub
End Module
We print 5 cars from the Cars table. We also save them
in an XML file.
Using da As New SqliteDataAdapter(stm, con)
A SqliteDataAdapter object is created. It takes an SQL
statement and a connection as parameters. The SQL statement will be used
to retrieve and pass the data by the SqliteDataAdapter.
Dim ds As New DataSet() da.Fill(ds, "Cars")
We create the DataSet object. The Fill method
uses the data adapter to retrieve the data from the data source. It creates
a new DataTable named Cars and fills it with the
retrieved data.
Dim dt As DataTable = ds.Tables("Cars")
The Tables property provides us with the collection of
data tables contained in the DataSet. From this collection
we retrieve the Cars DataTable.
dt.WriteXml("cars.xml")
We write the data from the data table to an XML file.
For Each row As DataRow In dt.Rows
For Each col As DataColumn In dt.Columns
Console.Write(row(col) & " ")
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Next
We display the contents of the Cars table to the
terminal. To traverse the data, we utilise the rows and
columns of the DataTable object.
Loading XML data
We have shown how to save data in XML files. Now we are going to show, how to load the data from an XML file.
Option Strict On
Imports Mono.Data.Sqlite
Imports System.Data
Module Example
Sub Main()
Dim cs As String = "URI=file:test.db"
Using con As New SqliteConnection(cs)
con.Open()
Dim ds As New DataSet()
ds.ReadXml("cars.xml")
Dim dt As DataTable = ds.Tables("Cars")
For Each row As DataRow In dt.Rows
For Each col As DataColumn In dt.Columns
Console.Write(row(col) + " ")
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Next
con.Close()
End Using
End Sub
End Module
We read the contents of the cars.xml file into the
DataSet. We print all the rows to the terminal.
Dim ds As New DataSet()
A DataSet object is created.
ds.ReadXml("cars.xml")
The data from the cars.xml is read into the data set.
Dim dt As DataTable = ds.Tables("Cars")
When the data was read into the data set a new DataTable
was created. We get this table.
For Each row As DataRow In dt.Rows
For Each col As DataColumn In dt.Columns
Console.Write(row(col) + " ")
Next
Console.WriteLine()
Next
We print all the rows of the data table.
$ mono loadxml.exe 1 Audi 52642 2 Mercedes 57127 3 Skoda 9000 4 Volvo 29000 5 Bentley 350000
Running the example.
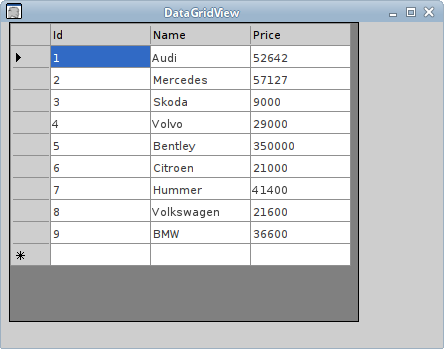
DataGridView
In the next example, we are going to bind a table to
a Winforms DataGridView control.
Option Strict On
Imports System.Windows.Forms
Imports System.Drawing
Imports System.Data
Imports Mono.Data.Sqlite
Public Class WinVBApp
Inherits Form
Private dgv As DataGridView
Private da As SqliteDataAdapter
Private ds As DataSet
Public Sub New()
Me.Text = "DataGridView"
Me.Size = New Size(450, 350)
Me.InitUI()
Me.InitData()
Me.CenterToScreen()
End Sub
Private Sub InitUI()
dgv = New DataGridView()
dgv.Location = New Point(8, 0)
dgv.Size = New Size(350, 300)
dgv.TabIndex = 0
dgv.Parent = Me
End Sub
Private Sub InitData()
Dim cs As String = "URI=file:test.db"
Dim con As New SqliteConnection(cs)
Dim stm As String = "SELECT * FROM Cars"
Using con As New SqliteConnection(cs)
con.Open()
ds = new DataSet()
Using da As New SqliteDataAdapter(stm, con)
da.Fill(ds, "Cars")
dgv.DataSource = ds.Tables("Cars")
End Using
con.Close()
End Using
End Sub
Public Shared Sub Main()
Application.Run(New WinVBApp)
End Sub
End Class
In this example, we bind the Cars table to the Winforms
DataGridView control.
Imports System.Windows.Forms Imports System.Drawing
These two namespaces are for the GUI.
Me.InitUI() Me.InitData()
Inside the InitUI method, we build the user
interface. In the InitData method, we connect
to the database, retrieve the data into the DataSe
and bind it to the DataGrid control.
dgv = New DataGridView()
The DataGridView control is created.
Dim stm As String = "SELECT * FROM Cars"
We will display the data from the Cars table in the
DataGridView control.
dgv.DataSource = ds.Tables("Cars")
We bind the DataSource property of the DataGridView
control to the chosen table.
In this part of the SQLite Visual Basic tutorial, we have worked with
the DataSet, DataTable, SqliteDataAdapter,
SqliteCommandBuilder, and DataGridView classes.